To Calculate The Masses Of Stars In A Binary Systemwe Must Measure Their
To calculate the masses of stars in a binary systemwe must measure their. If a parallax of 05 is observed for the star system what is its combined mass in solar masses. Convert to solar masses. Careful measurements reveal that a star maintains a steady apparent brightness at most times except that at precise intervals of 73 hours the star becomes significantly dimmer for about 2 hours.
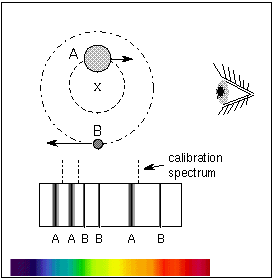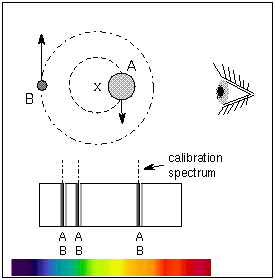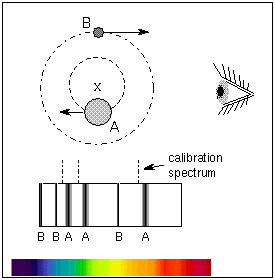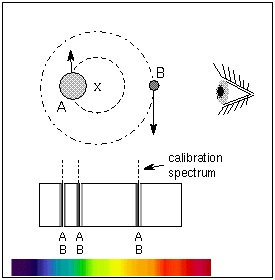
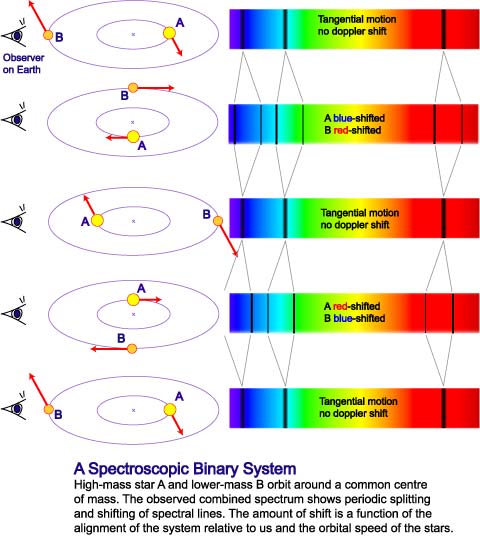
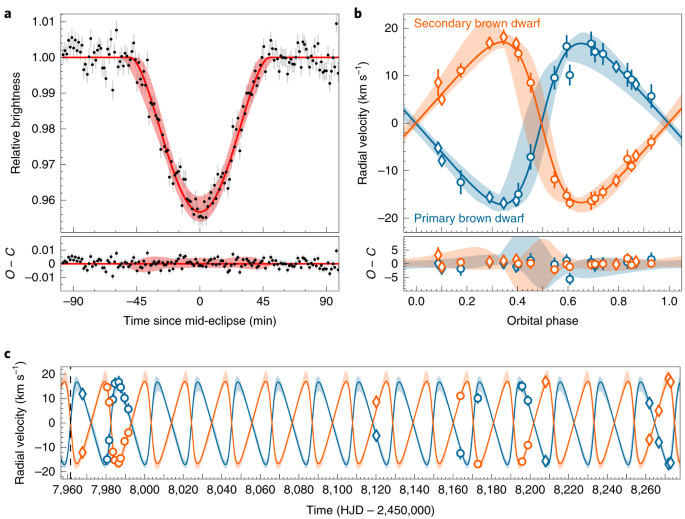
Newtons laws of motion Fma allow us to derive Keplers equation for orbital motion. Then the relative speeds of the two stars can be measured using the Doppler effect. Thus for a given age of the system we have one solution for the mass of the primary star M 1 and using QM 2 M 1 we can derive the mass of the secondary.
The speed will be inversely proportional to the mass. To calculate the masses of stars in a binary system we must measure their _____. This allows us to calculate the mass of each.
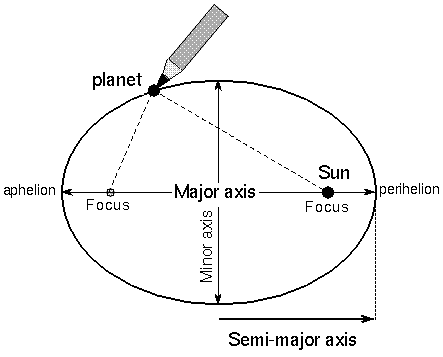
If we adapt them for a binary system where the masses of the component stars are similar then. The resultant masses are lower limits on the masses absent the value of cosi. M 1 M 2 x P 2 a 3 where.
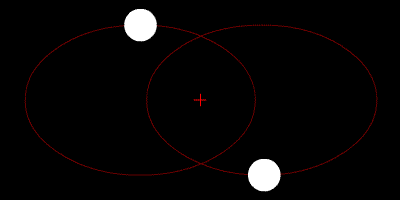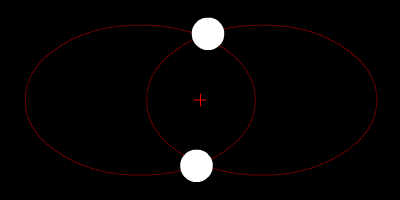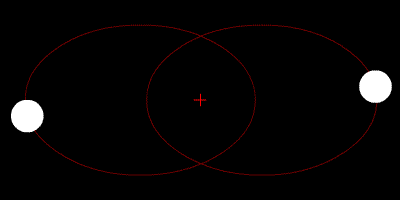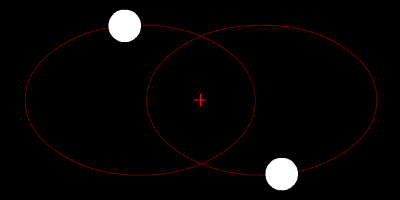
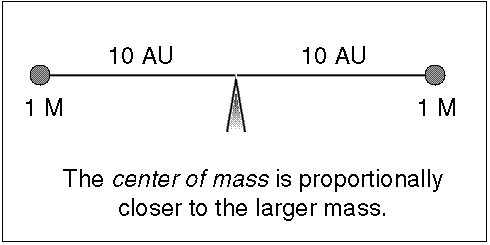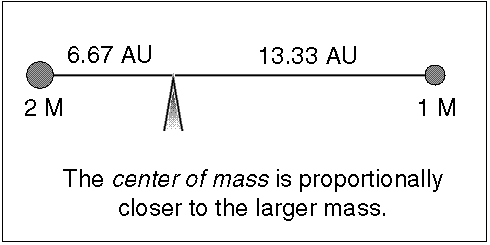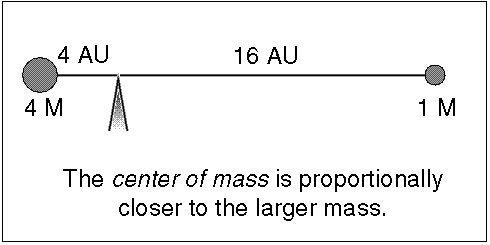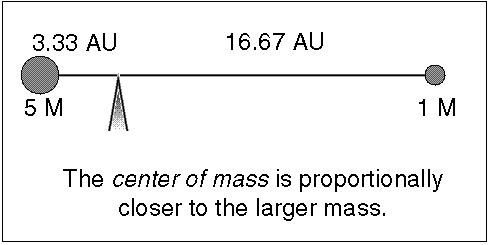
At their furthest they are 18 apart. Solve for m B mass of Sirius B in terms of cosi. Their common center of mass.
The physics that govern the stars orbits in a binary system or a planets orbit in a planetary system were developed by Newton and Kepler. Using the mass-luminosity relationship calculate. Masses of binary stars can be calculated from measurements of their orbits just as the mass of the Sun can be derived by measuring the orbits of the.
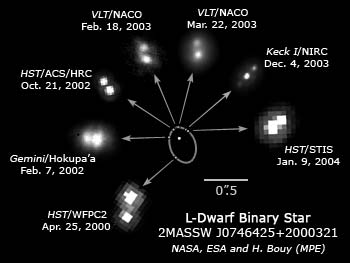
Here are two movies showing simulationsof visual binary stars one with a. However the age of the system must be constrained by other means.
Once this is done Keplers third law gives the sum of the masses of the two stars.
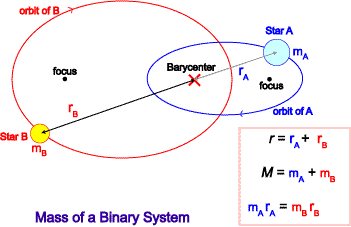
Assume an inclination of 90 degrees. Convert to solar masses. At their furthest they are 18 apart. If we measure the separation between the objects a and the period of their orbit P we can calculate their masses. In the previous section we determined the sum of the masses of the two stars in the Sirius binary system Sirius and its faint companion using Keplers third law to be 32 solar masses. In a nearby star system two stars are seen to orbit each other every 8 years. M 1 M 2 is the sum of. At their closest the stars are 2 apart. Relative positions about the center give.
Calculate a B distance of Sirius B from the barycentre and find the ratio of the masses of the two stars. Using the mass-luminosity relationship calculate. To find out the mass of each individual star astronomers need to know the mean distance of each star from the barycenter. However be used to estimate stellar masses. To learn this once again they rely on their. P2 4π2 Gm1 m2 r3 111 where P is the orbital period of the system r is the separation between the two stars and m1 m2 is the. Orbital period and average orbital distance.























Post a Comment for "To Calculate The Masses Of Stars In A Binary Systemwe Must Measure Their"